- For our products
Regulations
EN 1317–3
EN 1317–3 covers requirements for crash cushions, how they shall be tested and how their properties are to be described.
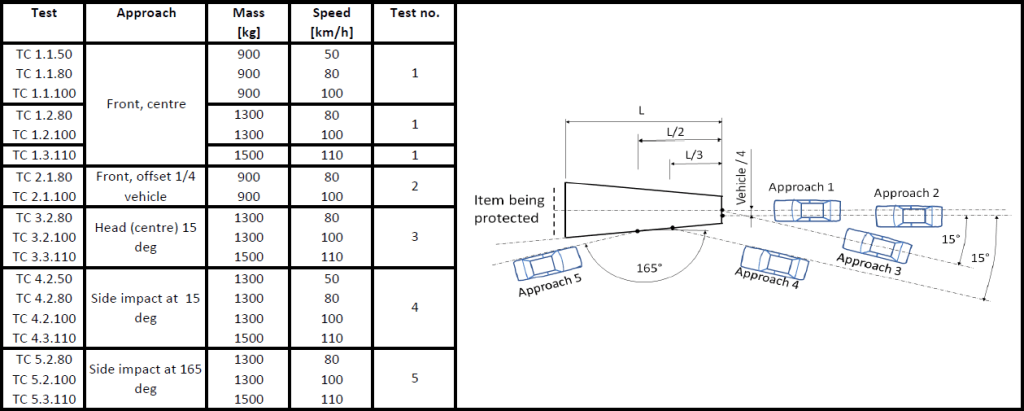
Test
The standard defines 18 different tests for crash cushions. These are named TC (Test Crash cushion) followed by a three digit number. The first figure tells the approach (1 to 5), the second type of vehicle (1 – 900 kg car, 2 – 1300 kg car and 3 – 1500 kg car) and the third and last tells the test speed (50, 80, 100 or 110 km/h).
Example:
TC 1.1.50: TC (Test Crash cushion), Test 1, vehicle type 1 (car 900 kg), 50 km/h
TC 3.3.110: TC (Test Crash cushion), Test 3, vehicle type 3 (car 1500 kg), 110 km/h
Tests using approach 4 and 5 are only performed on redirective crash cushions, a type required in Sweden.
Impact severity level
The Impact severity level gives an assessment of how safe a crash cushion is for occupants in an impacting vehicle. Thera are two levels, A and B. Impact severity level A is the safest for occupants in an impacting vehicle.
Most crash cushions fulfil requirements for impact severity level B. In Sweden both impact severity lever A and B are accepted.
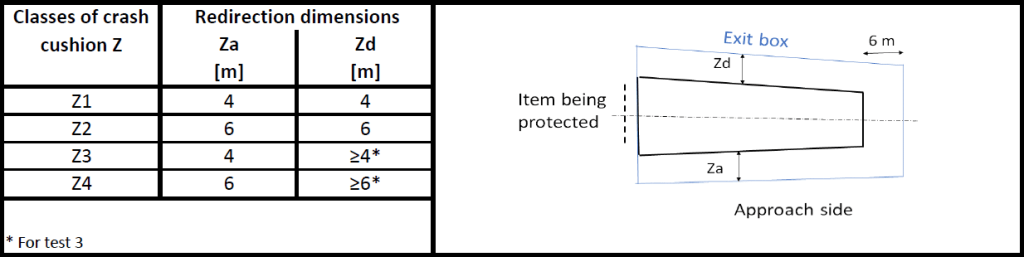
Class of lateral displacement
The permanent lateral displacement of the crash cushion shall be as shown in the table below. In the permanent lateral displacement also detached parts equal to or greater than 2 kg are included.
In Sweden the class of lateral displacement shall be chosen in such a way that a deformed (impacted) crash cushion does not intrude on adjacent carriageways or covers more than the width of adjacent pedestrian/bicycle paths minus one meter.